First published in PTQ Catalysis 2023
Sophie Babusiaux, Hydroprocessing Technology Advisor, Axens
Lucas Vergara, Principal Technology Engineer, Axens
Processing and co-processing renewable feedstock is part of today’s main refineries’ strategies to reduce the carbon footprint of their activities. As defined by the European Union, second- and third-generation biofuels are produced from feedstock that does not compete directly with food and feed crops, such as wastes and agricultural residues (wheat straw, municipal waste), non-food crops (miscanthus and short rotation coppice), and algae.
The starting point strategy to integrate these feeds into a refinery is first to identify the local availability and individual feed challenges. Then, depending on the conversion/ hydroprocessing platforms available at site, look for the most suitable unit to cope with these in terms of existing hardware and impact on products. To be sure, more than 50 years of providing solutions in optimizing refinery refining schemes throughout the world delivers the repository of experience, know-how, and methodology to conduct detailed dedicated studies in a constantly evolving legislation framework.
Processing second- and third-generation biofeeds represents specific challenges to the operation, for both new units and retrofits, either in co-processing or stand-alone mode. The design shall consider robust and proven solutions. We have developed solutions over the past 30 years to prevent pressure drop, loss of activity, corrosion, and other nuances that have emerged in the processing of renewable feedstock.
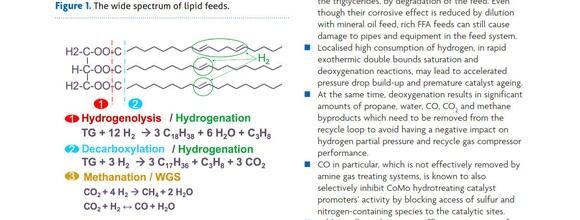
Catalytic solutions to help tackle the challenges associated with co-processing sustainable feeds
Technical Article - The role of integrated and derisked technologies as a cornerstone of eFuels deployment
Technical Article - Vegan technology: low-carbon solution for renewable diesel and SAF
Webinar - Strategic Pathways to Secure SAF Production Technologies
How Energy Transition and Product Diversification Planning Affect Revamp Projects?
Case Study - Producing Renewable Liquid Products From Different Lipid Feedstocks Through a Revamp
Read moreCase Study - Feasibility Study Of A Standalone Biorefinery For MGH Based On Axens’ Biofuel Technologies Portfolio Vegan® And Futurol™
Read moreWhite Paper - Solutions for More Sustainable Transportation Fuels and Chemicals
Technical Article - The role of integrated and derisked technologies as a cornerstone of eFuels deployment
Technical Article - Vegan technology: low-carbon solution for renewable diesel and SAF
Technical Article - SAF: Finding scalable solutions
Technical Article - Connecting the Dots to Bankability with Low-Carbon Bio-Hubs for Sustainable Fuels and Chemicals
How Energy Transition and Product Diversification Planning Affect Revamp Projects?
What FCC and hydrotreater modifications are needed to increase refinery coprocessing of renewable feedstocks?
What are some of the optimal strategies for processing (or co-processing) second- and third-generation renewable feedstocks?
How can the refining industry supply the aviation industry’s growing demand for sustainable aviation fuel (SAF)? What are the most efficient pathways?
Advancing SAF in Asia: Axens Becomes a Gold Member of ASAFA
Gevo and Axens Partner to Broaden Their Alliance to Develop and Commercialize Bio-Based Renewable Hydrocarbon Fuels and Also Develop Gevo’s ETO Technology
Axens tapped for 3 new Vegan® licenses by Galp, LOKEN and SAFCO Ventures, for SAF and Renewable Diesel Production
SAF: KazMunayGaz and Axens extend collaboration
Webinar - Strategic Pathways to Secure SAF Production Technologies
Read morePodcast - Scaling up through demo plants: Mitigating risks associated with new technologies
Read more