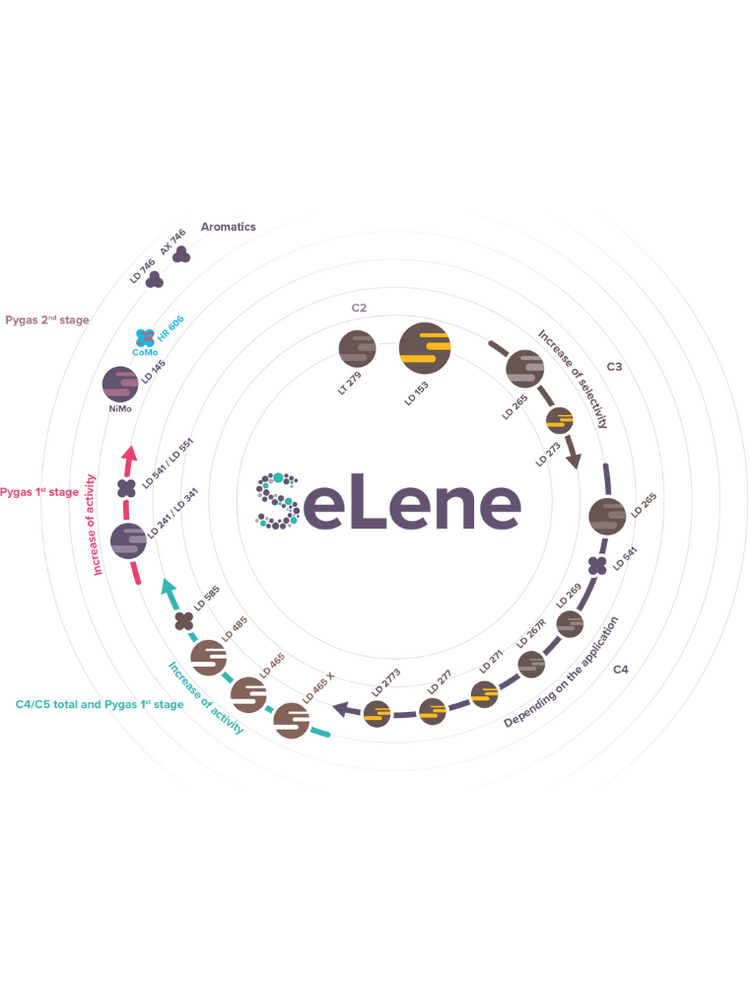
SeLene™
SeLene™, Axens’ Selective Hydrogenation Catalysts Family, features the highest activity and lowest density on the selective hydrogenation catalyst market, allowing the highest level of performance while minimizing the cost to fill and maximizing energy cost savings.
More than 50 years in research and development and unit design have led to unmatched results with more than 750 worldwide license references and 850 worldwide catalysts references, for a cumulative onstream operating experience exceeding 30 MM hours.
C₂ Selective Hydrogenation
C₂ Selective Hydrogenation
C₃ Selective Hydrogenation
C₃ Selective Hydrogenation
In addition to containing up to 90% propylene, steam cracker C3 cuts contain from 2 to 8% methylacetylene and propadiene (MAPD). Selective hydrogenation of MAPD aims to remove MAPD through its hydrogenation to propylene.
Valorization of C3 Cut Valorization for Light Cuts
C₄ Selective Hydrogenation
C₄ Selective Hydrogenation
C4 cuts may be produced by steam crackers, fluidized catalytic crackers (FCC) unit or butane dehydrogenation units. These streams contain mainly olefins and paraffins, as well as diolefins (butadiene) and occasionally vinylacetylene (VAC).*
Valorization of C4 Cut Valorization for Light Cuts
Pyrolysis Gasoline Hydrogenation
Pyrolysis Gasoline Hydrogenation
Ethylene production by steam cracking produces several by-products such as pyrolysis gasoline (pygas). Raw pygas contains highly valuable components such as BTX (benzene, toluene, xylenes), unsaturated compounds like diolefins, styrenics and olefins, and sulfur-containing compounds. In order to recover BTX, the unsaturated compounds and sulfur compounds have to be removed efficiently. This is the target of Axens’ catalysts through two different stages of pygas hydrogenation.
Arofining®
Arofining®
An important source of aromatics for petrochemical end-uses originates from high severity, continuous catalyst regeneration (CCR) reformers. The current trend towards high severity operation results in higher concentrations of undesired unsaturated hydrocarbons (diolefins, olefins, styrenes) in the reformate produced. These unsaturated hydrocarbons are selectively hydrogenated while minimizing the aromatic loss.
The selective hydrogenation can be implemented on the full reformate or any individual aromatics fraction depending on specific needs.
Other Selective Hydrogenation
Other Selective Hydrogenation
Resources
What could be causing rapid catalyst deactivation in the hydrogenation of heavier fractions downstream of our steam cracker furnace?
Technical Article - Catalytic Answer To A Steam Cracking Challenge
100th Award of Axens Solutions’ Latest Generation of High Performance Selective Hydrogenation Catalysts
100th Award of Axens Solutions’ Latest Generation of High Performance Selective Hydrogenation Catalysts
Technical Article - Catalytic Answer To A Steam Cracking Challenge
What could be causing rapid catalyst deactivation in the hydrogenation of heavier fractions downstream of our steam cracker furnace?
You Might Be Interested In
Drying Series Adsorbents
Purification Series Adsorbents
Speciality Bed Topping
TO CONTACT US
Please fill in the contact form below